Abstract
Previous evidence suggests that the thromboembolic risk is greater among patients with COVID-19 than among those affected by other types of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). However, such comparison has been primarily based on historical cohorts. In order to reduce the possible influence of such selection bias, the main goal of this study was to evaluate thromboembolic events in patients with COVID-19 and other ARDS hospitalized in the same time period.
For this reason, we have selected patients admitted from March to June, 2020 at the UNICAMP Clinical Hospital who met the ARDS clinical criteria established by the Brazilian Ministry of Health and the Berlin Definition by presenting two or more flu-like symptoms and at least one ARDS-specific manifestation (dyspnea, persistent chest pressure, oxygen saturation lower than 95% at hospital admission, or lip/face cyanosis). Symptom onset or worsening occurred 30 days before hospital admission at the latest, and COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed or excluded by at least 2 real time polymerase chain reactions or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Descriptive analysis, chi-square and t-tests, as well as binary logistic regression, were used to compare COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients.
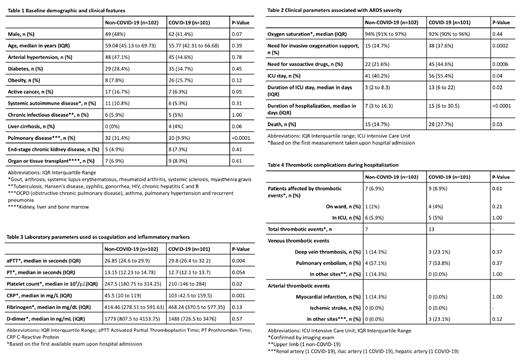
Of the 253 patients hospitalized due to ARDS during this period, 101 COVID-19 and 102 non-COVID-19 patients were included in this study. The remaining patients were excluded due to incomplete medical records (n=16) or absence of COVID-19 testing results (n=34). Table 1 demonstrates the included patients' demographic and clinical baseline features.
Both COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 groups showed similar baseline risk of hospital-associated thrombosis (assessed by reduced mobility within the past 3 days or more, previous thromboembolism event, recognized "thrombophilia", and infarction, stroke, trauma or surgery within the past 4 weeks) and oxygen saturation at admission (COVID-19: 92% IQR 90% to 96%; non-COVID-19: 94% IQR 91% to 97%, P=0.44). However, the need for invasive oxygenation support (37.6% vs. 14.7%, P=0.0002) and vasoactive drugs (44.6% vs. 21.6%, P=0.0006) was greater in COVID-19 than in non-COVID-19 patients. Accordingly, those infected by SARS-CoV-2 were more frequently admitted in ICU (55.4% vs. 40.2%, P=0.04) and for a longer period of time (13 days IQR 6 to 22 vs. 3 days IQR 2 to 8.3, P=0.02) than those affected by other types of ARDS. In comparison to the non-COVID-19 group, the COVID-19 group's median total hospital stay was more lasting (15 days IQR 6 to 30.5 vs. 7 days IQR 3 to 16.3, P<0.0001), and its death rate, higher (27.7% vs. 14.7%, P=0.03), as shown in Table 2.
With respect to coagulation markers (Table 3), activated partial thromboplastin time and C-reactive protein levels were greater in COVID-19 than in non-COVID-19 patients, while the latter presented higher median platelet counts. There was no statistically significant difference between both study groups in regards to prothrombin time, fibrinogen, and D-dimer levels (COVID-19: 1488 ng/mL IQR 726.5 to 3476; non-COVID-19: 1773 ng/mL IQR 807.5 to 4153.8, P=0.57).
Although thromboprophylaxis was more commonly administered to COVID-19 (76.2%) than non-COVID-19 patients (41.2%, P<0.0001), the incidence of thromboembolic events confirmed by imaging examination was similar between groups even after adjusting for multiple factors (age, sex, thromboprophylaxis use, arterial hypertension, and cancer): there were 7 confirmed events in 7 non-COVID-19 patients, and 13 confirmed events in 9 COVID-19 patients (adjusted OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.24-2.25, P=0.59). Table 4 demonstrates the characteristics of such thrombotic manifestations.
By analyzing patients hospitalized in the same time period, we have found that although high, the thromboembolic risk in COVID-19 is similar to that in other types of ARDS, indicating that a hypercoagulable state is inherent to ARDS in general. Additionally, the obtained results show that the use of thromboprophylaxis was significantly higher among COVID-19 patients, and that there was no statistically relevant difference between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients' D-dimer levels, a commonly used coagulation marker. Such findings provide a better understanding of the thromboembolic risk associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, and suggest that previous evidence of higher thrombosis rates in COVID-19 suffered bias from the use of historical cohorts.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal